Everything that you paint should tell a real story, one that is authentic to you.
| Big-boned, by Carol L. Douglas. As soon as I finish my taxes, I’ll be back at the boatyard painting schooners. |
There is something about being in our favorite place that transcends detail. We know it by feeling rather than by specifics. As artists we are attempting to recreate that sense of place using only visual cues. That requires specificity and accuracy.
Artists become expert in oddly arcane matters. Marilyn Fairman can identify all the birds that sing in the understory. She told me she learned from one of those silly clocks they used to sell with a different bird call for every hour. And she paints without headphones on, so that she can hear the sounds of nature.
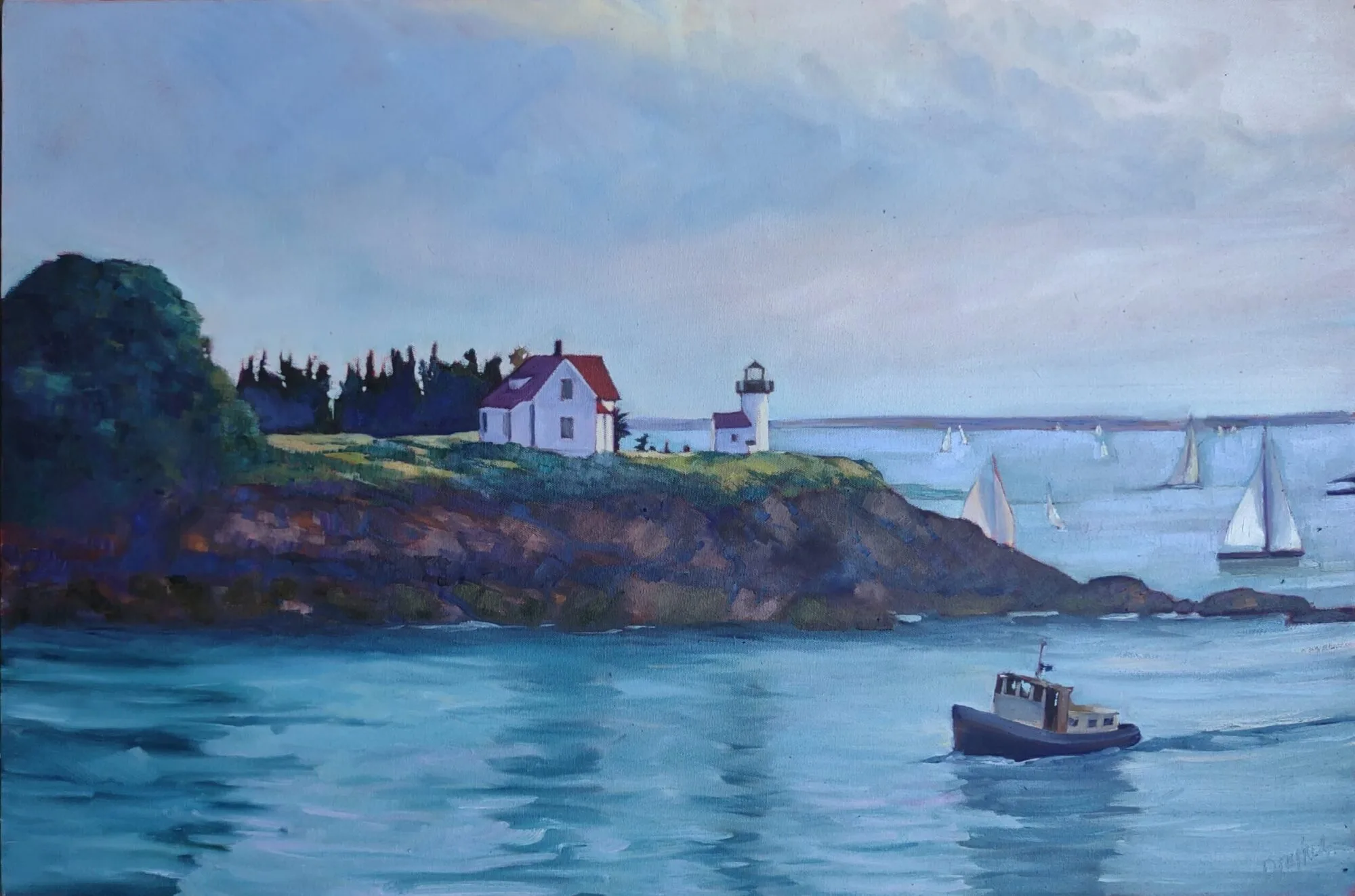
Sandra Hildreth of Saranac Lake is expert on the topography of the High Peaks region. She got that way because she has hiked all over the Adirondacks. Likewise, Bobbi Heath knows lobster boats because she’s spent serious time cruising and painting the waters of Maine.
 |
| Winch, by Carol L. Douglas |
I can’t say I know any of those things encyclopedically, but I’m pretty strong on trees and rocks. So if you bring me a painting with brown, undefined lumps where the granite of Maine or the red sandstone of the Minas Basin should be, I’m bound to say something.
Isn’t the important thing that you create a pleasing painting? That’s true, but squidging the details is amateurish. What’s the point of painting the Canadian Rockies if they end up looking like New Mexico? Last week, I mentioned Paul Cézanne’s sixty paintings of Mont Sainte-Victoire. He experimented in all of them, but the mountain remains recognizable.
 |
| Coast Guard Inspection, by Carol L. Douglas |
“Sense of place” is a phenomenon that we can’t define, but we all know when we see it. As individuals, families, and a culture, we set aside certain places as being exceptional. It’s why we have World Heritage Sites, National Parks, and National Scenic Byways.
When a place is without character, we sometimes say it is “inauthentic.” Once again, we can’t define that, but we all seem to know them when we see them: shopping malls, fast food restaurants, or new housing tracts. As Gertrude Stein once said, “There is no there there.”
| More work than they bargained for, by Carol L. Douglas |
How does a scene achieve a “sense of place” in our consciousness? It acquires a story, which is a finely- crafted pastiche of memory, events, and beauty. Our childhoods, in particular, shape our adult response to the physical world. Psychologists call the setting of our childhood our primal landscape. It becomes the bar against which we measure everything we see thereafter.
All of this argues against painting an anodyne landscape. And it argues for landscapes with lodestars. If you’re honest with your feelings, a lighthouse or grain elevator will not end up being clichéd.
Everything that you paint should be something that you’ve experienced. It should tell a real story, one that relates back to you. Your canvas is not just a rectangle that you fill up with generic ‘nature’. It should be a little slice of a place.
Note: my websiteis completely updated. It’s new work and a new, mobile-friendly platform, too. Won’t you take a peek?