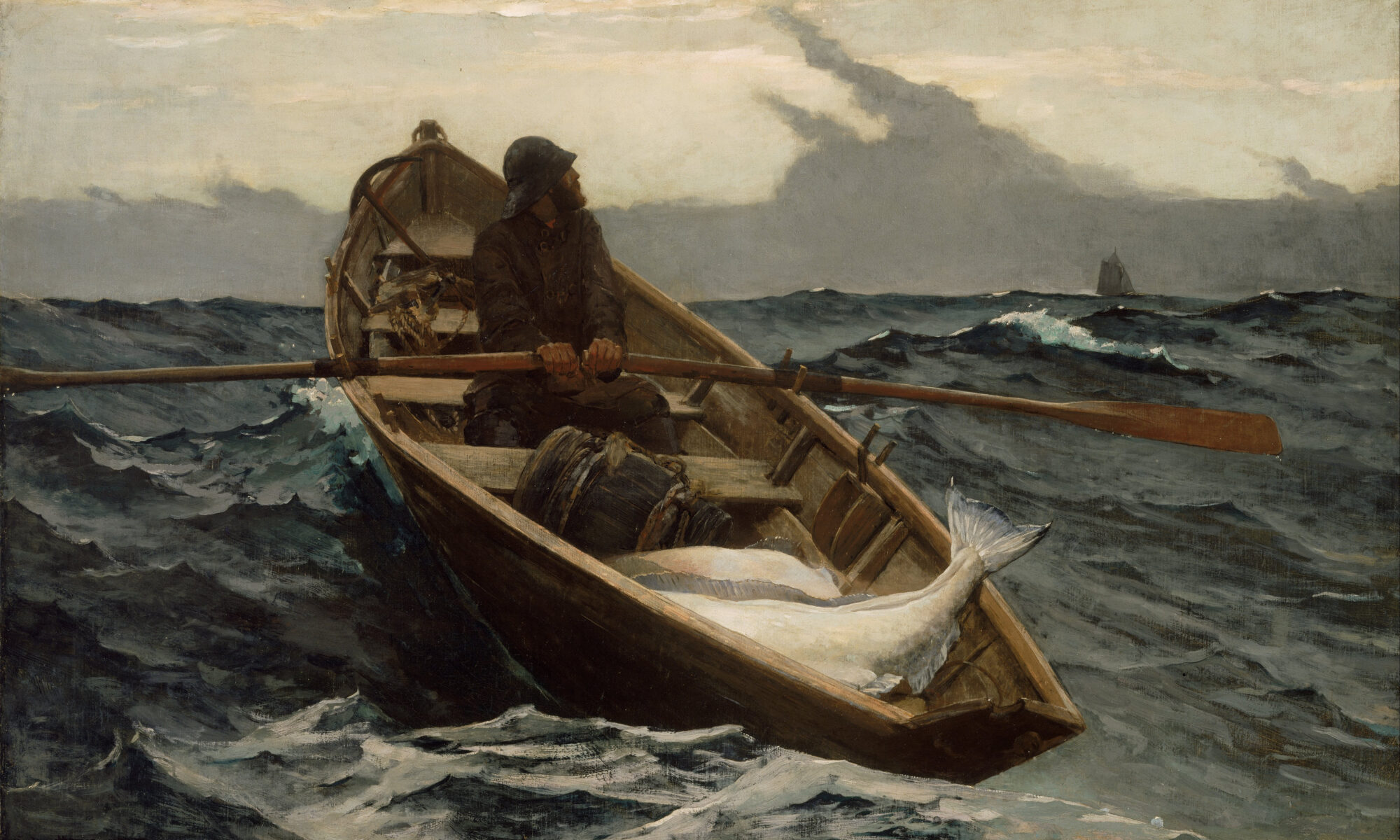
In our narrative painting class on Monday, Bobbi Heath told us about a man who didn’t want anyone in the dinghy in his painting. “I want to be able to imagine myself in it,” he said.
In addition to portraiture, there are several ways in which one can approach the figure in painting, including:
- A specific individual serving as an archetype, as in Mary Whyte‘s paintings.
- Through a vague, implied, incomplete or anodyne figure, as in Andrew Wyeth‘s Trodden Weed or Winslow Homer‘s The Fog Warning, above.
- Through objects or settings that suggest an imminent arrival, as in that empty dinghy or George Stubbs‘ A Saddled Bay Hunter, below.

It’s one thing to paint a pretty picture. It’s another to blur the line between the audience and the scene, to paint something where the viewer can step into the frame and build a relationship with the work.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Mona Lisa is important to art history because of its use of landscape, its sfumato and its anatomical accuracy. That doesn’t explain its enduring popularity. Mona Lisa resonates because we engage with her.
The subject makes eye contact with us, with a rather penetrating gaze. She’s not demure, she’s not dreamy, and she’s not dressed to advertise her femininity, wealth or power. (As an aside, I’m sure this is why we get the periodic daft theory that it is a concealed self-portrait of the artist; after all, what mere woman could be that self-assured?)
Mona Lisa invites you to have a parasocial relationship with the subject. That’s a modern term for a one-sided relationship with a person we don’t know, usually an influencer, celebrity, or fictional character. We project attitudes, values, and beliefs onto them, just as we project them onto Mona Lisa.

The word ‘voyeur’ wasn’t created until a few centuries after Johannes Vermeer was painting. His intent wasn’t to titillate in that modern sense, but to create the kind of genre paintings that were so popular in his time. However, his perfect drafting and the subtle interactions of his figures make us feel like we’re looking through a peephole. That drags us almost violently into his paintings.
Edward Hopper picked up where Vermeer left off. Works like Hotel Room or Room in New York leave us feeling almost as if we’re peeping toms. It’s unlikely that in the early 1930s, that was Hopper’s intention. Incandescent lighting was just becoming widespread in New York . Hopper was fascinated by it, and by the jewel-like, illuminated scenes it created through city windows. But art has overtones that shift and change over time, regardless of the artist’s intentions.

In Hopper’s paintings we come full circle to the same incomplete or anodyne figures of Winslow Homer or Andrew Wyeth. If the woman on the bed in Hotel Room was detailed and realistic, she’d be almost unbearably vulnerable. Stylizing her preserves her, and our, dignity.
My 2024 workshops:
- Painting in Paradise: Rockport, ME, July 8-12, 2024.
- Sea & Sky at Schoodic, August 4-9, 2024.
- Find your authentic voice in plein air: Berkshires, August 12-16, 2024.
- Art and Adventure at Sea: Paint Aboard Schooner American Eagle, September 15-19, 2024.
- Immersive In-Person Workshop: Rockport, ME, October 7-11, 2024.