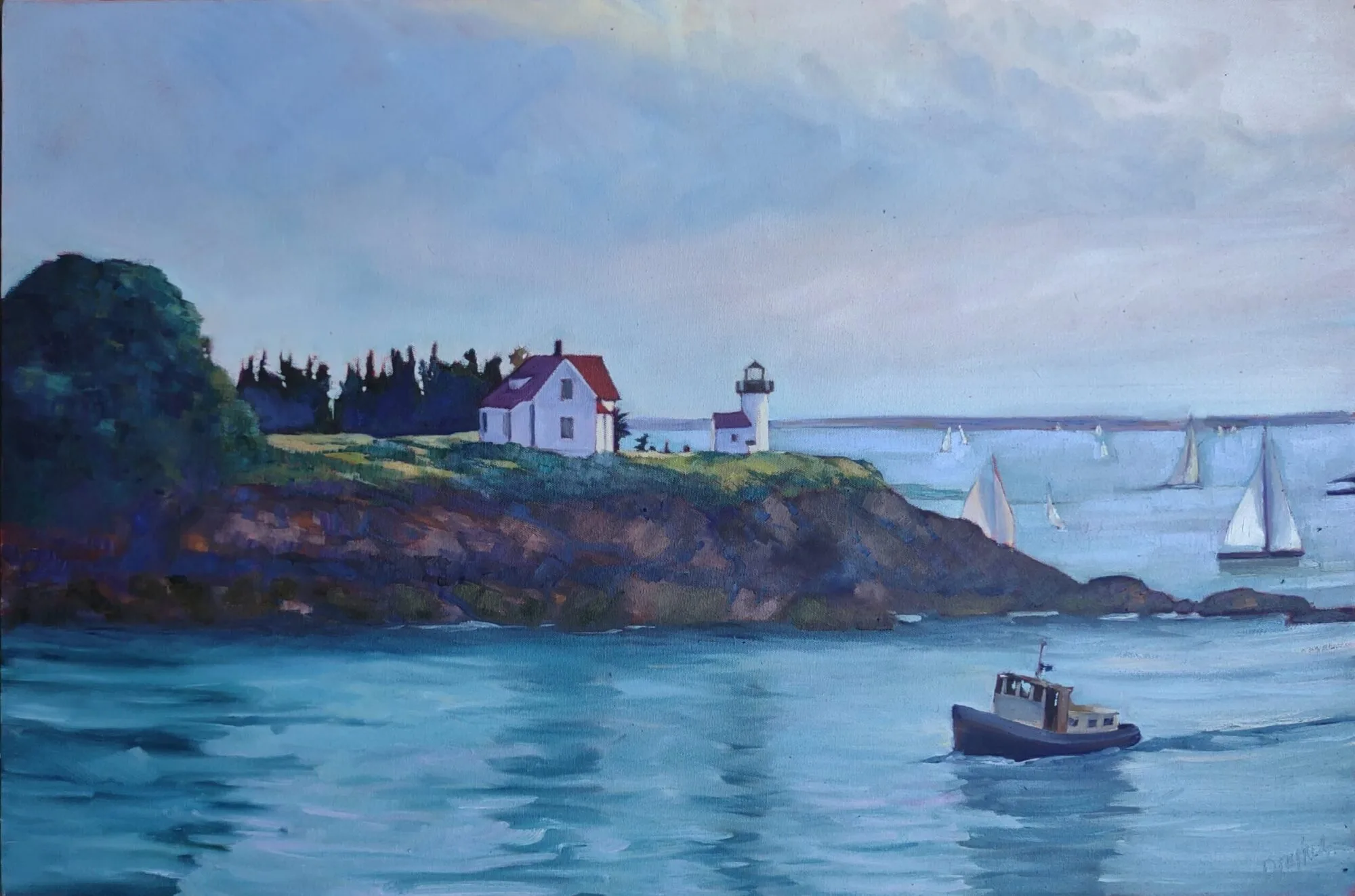
During last week’s workshop, Beth, Sharon and I were looking at a house on Pearl Street in Camden. I’d given them a lesson on two-point perspective and then said, “That’s just so you understand the principle. In real life, you’re going to measure angles rather than draw to a vanishing point.” That’s harder to do, because angle drawing takes practice. However, all drawing rests on angles and measurement.
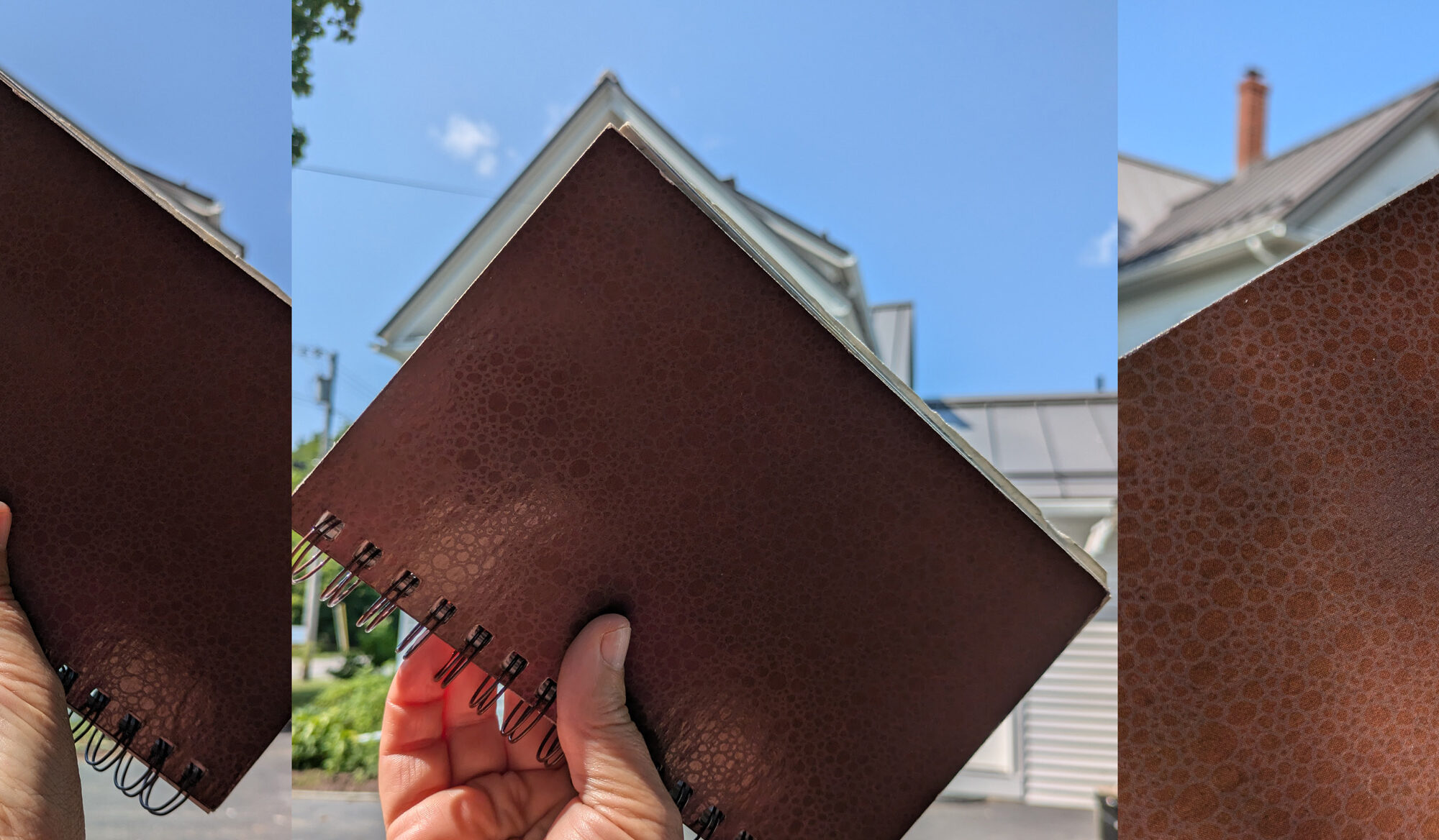
“That gable end looks like it’s at a 90° angle,” Sharon said. Beth and I immediately disagreed. Of course we were roughly twenty feet away from her, so what we were seeing wasn’t what she was seeing. I heaved myself up (it was a hot day) and looked at what she was doing. She was holding an L-shaped composition finder up to the sky. Immediately I grasped an important new idea.
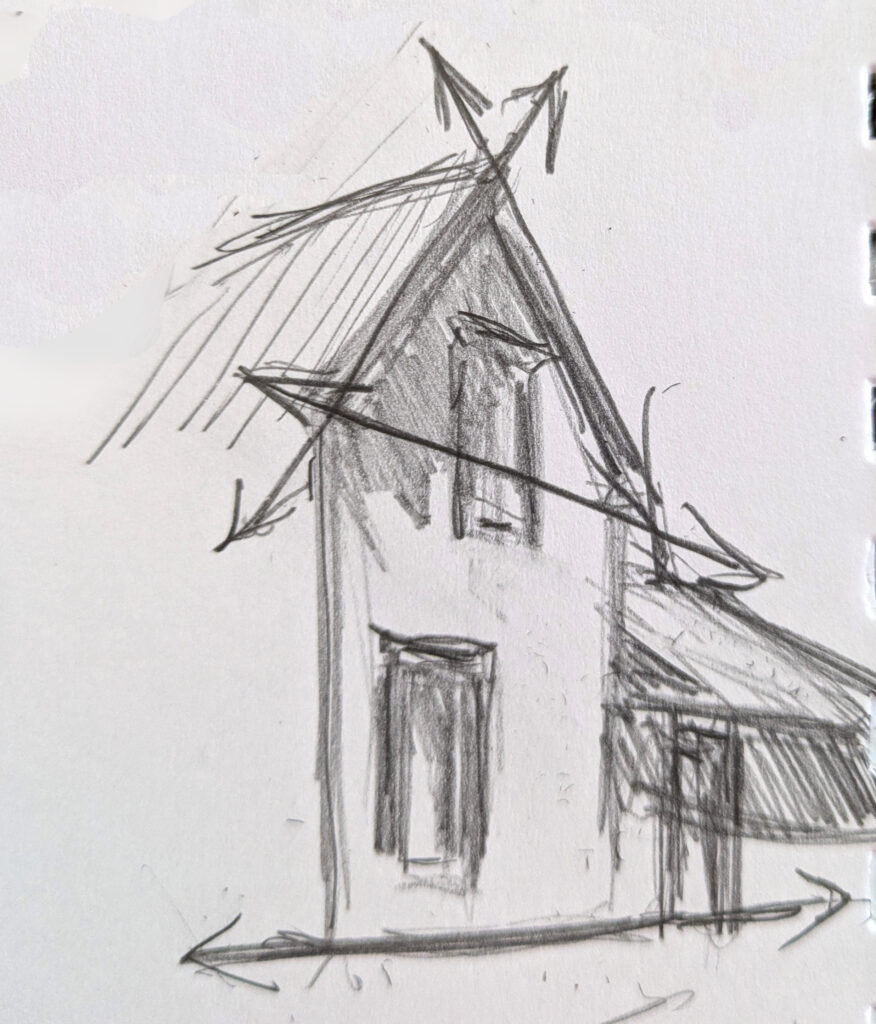

If you hold something that you know to be a right angle up to the angle you’re measuring, you can see how it deviates.
We’re all carrying around something that’s got a right angle: our sketchbooks. Failing that, we always have our cell phones.
Sharon’s view was, in fact, exactly 90°, but the idea was also useful to Beth and me. From our location, the angle formed by the gable end was about 10° flatter than Sharon’s view. I experimented holding my sketchbook up to various angles in the landscape and was pleased at how easily I could see angles.
(By the way, a roof where the gable end is at 90° looking straight-on would be a 12/12 pitch, which is pretty steep. Most of the time, when you see a 90° angle, it’s because you’re looking at it from off to one side.)
What if it’s so far off 90° that it’s hard to make a comparison?
I was on a roll, so I estimated other angles using Sharon’s idea. That was fine until I was so far off 90° that making a comparison no longer worked.
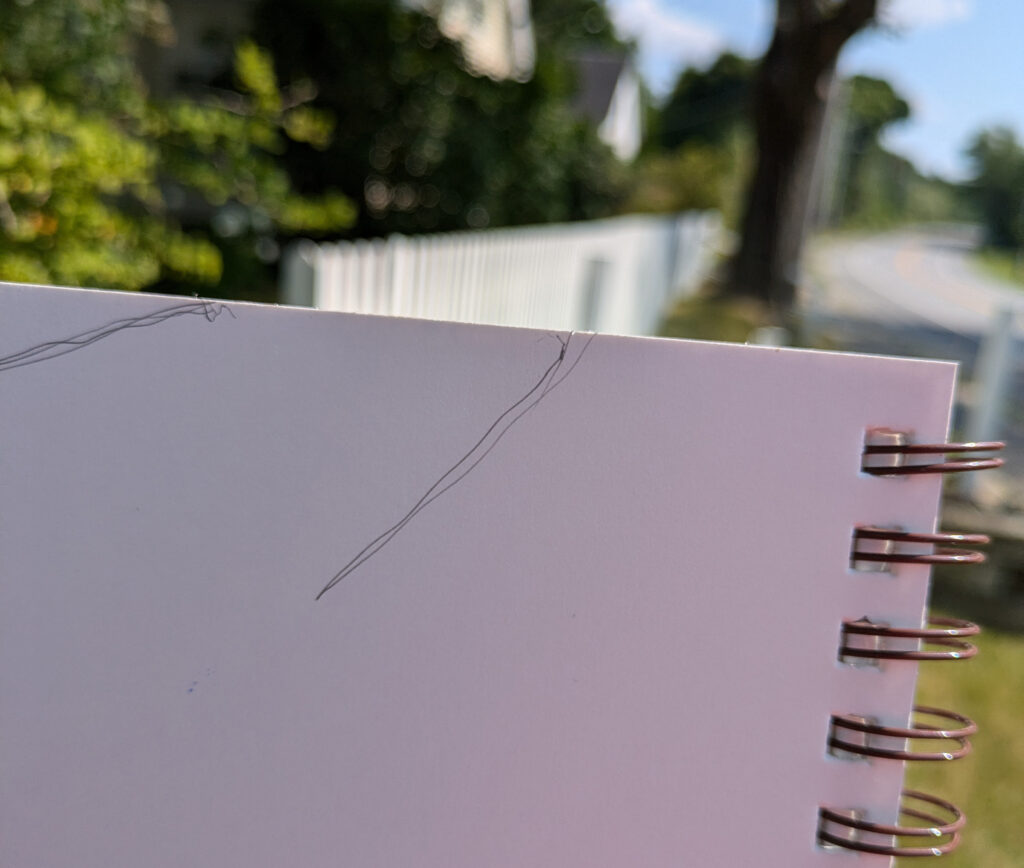

What if I held my sketchbook level with the ground and marked that angle as a hash mark in the corner, I asked myself. Then I can easily translate that line into a parallel one where it belongs in my sketch. And, yes, that worked too.
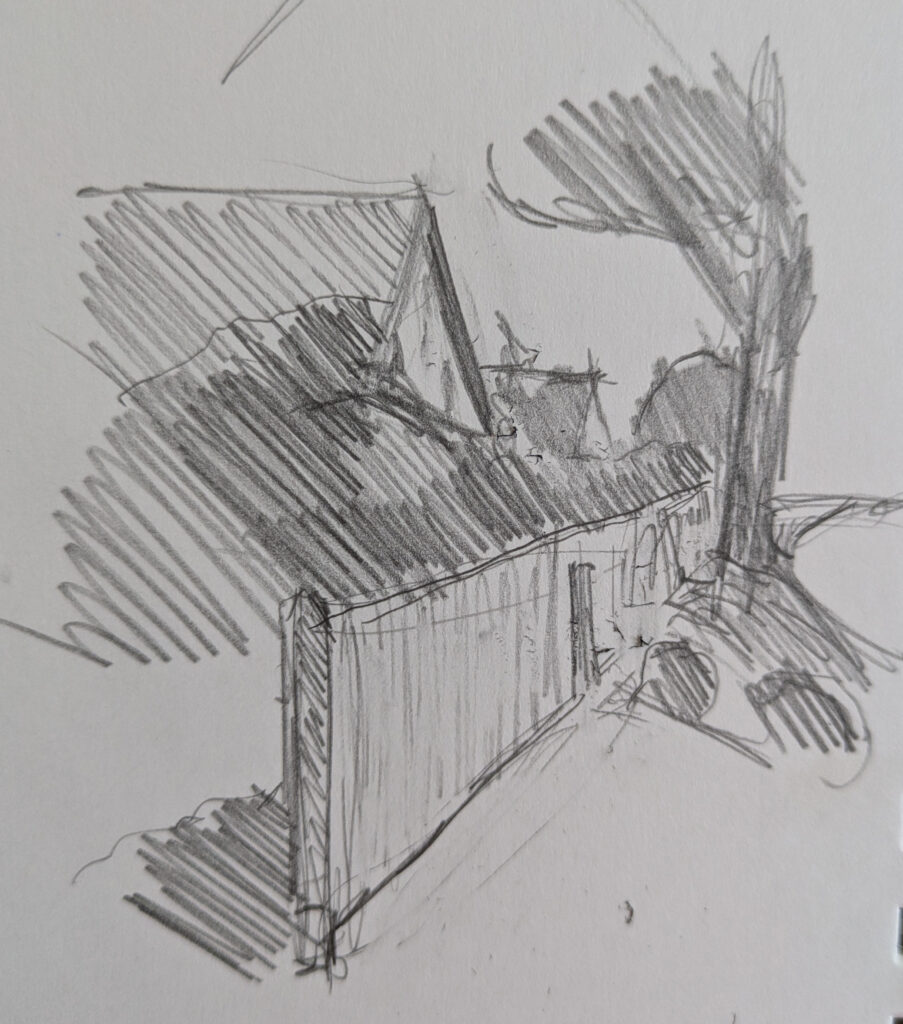
Angle drawing is important
Angles are critical to representing perspective. They also create the illusion of depth and space. Being able to sight-draw them allows us to draw objects from different viewpoints.
But, wait, there’s more. Angle drawing is important for:
Measurement: it’s often easier to see spatial relationships through angles than with the thumb-and-pencil method of drawing. (Fast, loose painting rests on a base of good drawing. If you haven’t been taught to measure with a pencil, start here, here and here.)
Anatomy: Angles are essential for capturing the relationships between different parts of the body. This is particularly important in drawing limbs, posture and facial features.
Shading: Angles influence how light falls on an object and how shadows are cast.
Dynamism: Angles contribute to a sense of movement and energy in a drawing.
Foreshortening: You can’t foreshorten an object if you can’t see the angles, period.
That means any trick that makes angle drawing easier, I’m going to use, and I hope you do, too. Thank you, Sharon.
My 2024 workshops:
- Sea & Sky at Schoodic, August 4-9, 2024.
- Find your authentic voice in plein air: Berkshires, August 12-16, 2024.
- Art and Adventure at Sea: Paint Aboard Schooner American Eagle, September 15-19, 2024.
- Immersive In-Person Workshop: Rockport, ME, October 7-11, 2024.